1. Define the problem behavior
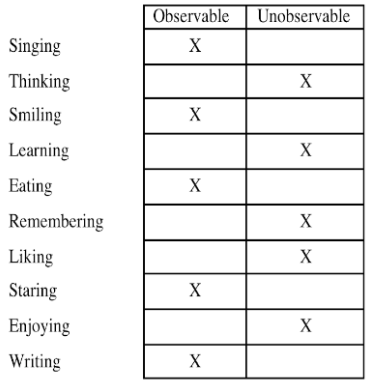
Behaviors must be described in observable and measurable terms.
When describing behaviors think about:
- Giving examples
- Setting of the behavior
- Topography
- Length of time
Two people should agree when the behavior occurs.
2. Collect assessment data
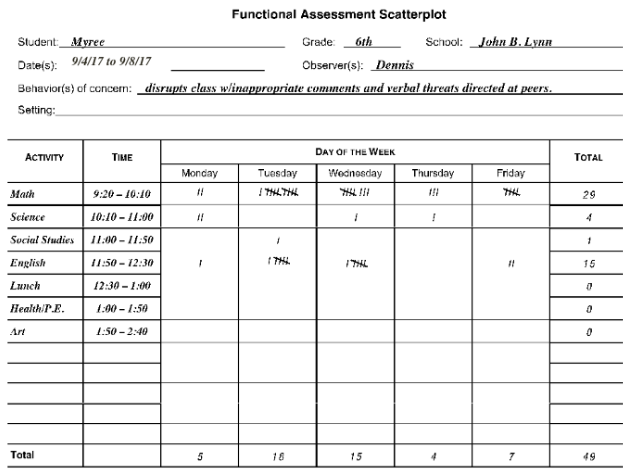
Indirect- Interviews, Behavior Rating Scales, File record review/Discipline history/Attendance, Academic level of functioning, Medical health history, Effectiveness of past services or interventions (academic and behavioral)
vs.
Direct- Direct Behavior Rating (DBR), ABC form, Scatter Plot Form
3. Analyze data

Analyze data for:
- Attention
- Escape/Avoid
- Stimulation
- Can't vs. Won't
What is the function? Use the following analysis tools to help find out:
Motivation Assessment Scale (LRBI)
Motivation Assessment Scale
Functional Analysis Screening Tool
4. Develop summary statement
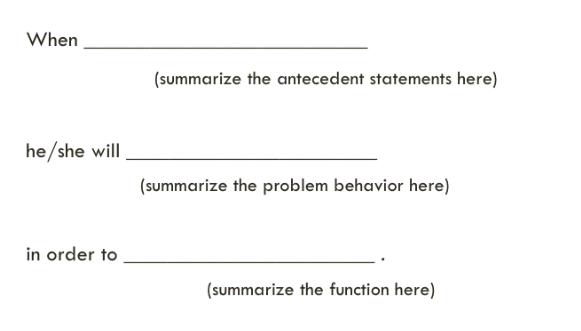
Hypothesis StatementWhen [Antecedent] occurs, the student [problem Behavior] in order to [Consequence (function)].
5. Identify replacement behavior
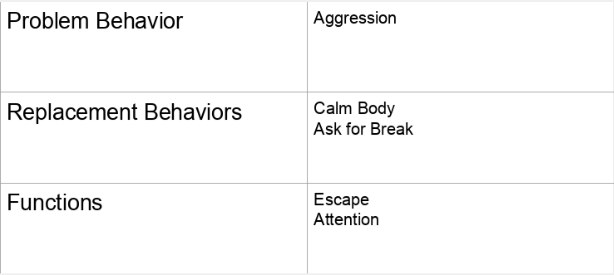
The replacement behavior
- is the behavior that you will be teaching the student to do instead.
- must serve the same function as problem behavior
